In today's market, a business trying to stay ahead with the updated technology and use all the market tools for flourishing in their growth has no dearth of options. SAP HANA or SAP High-performance Analytic Appliance is a fast and powerful database that renders multi-model, real-time data analytics.
SAP HANA provides a platform for Smart Data Integration (SDI) that makes data processing more manageable and faster than ever. This article will discuss how SAP HANA SDI works, its requirements, restrictions, features, and benefits.
What is SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI)?
SAP HANA holds data in memory instead of storing it on a disk. It thus results in fast data processing, and the magnitude becomes more instantaneous than the speed of the disk-based data systems, allowing for groundbreaking and real-time analytics.
SAP Smart Data Integration (SDI) is an engine that runs on the SAP HANA platform. Businesses can use it for data integration with SAP Commissions. It is a part of the HANA platform that enables transforming, receiving, and loading data to and from the SAP HANA database.
Its capabilities comprise loading high-volume data, high-speed data provisioning, real-time and batch data movement, and fast data transformation. SAP HANA platform provides Smart Data Integration with tools to access source data and provision, copy, and convert the data in SAP HANA on-premise or the cloud.
SAP Smart Data Integration (SDI) supports all kinds of data integration, such as Transform, Load or Extract, Bulk or batch Extract, real-time data replica, and data virtualization. Smart Data Integration operates on a database layer.
Developers can use the web-based interface provided by Smart Data Integration to design a data integration path to satisfy the requirements and needs of the customers.
What is the architecture of the Commission SAP HANA SDI?
Data loads in batches or real-time into the commission platform of HANA with the SAP SDI from flat files through pre-built and custom adapters. The SAP HANA system provision the Data Provisioning Agents that businesses use to house adapters and links to the source system with the Data Provisioning server.
The following diagram will explain the architecture of the Commission SAP HANA SDI:
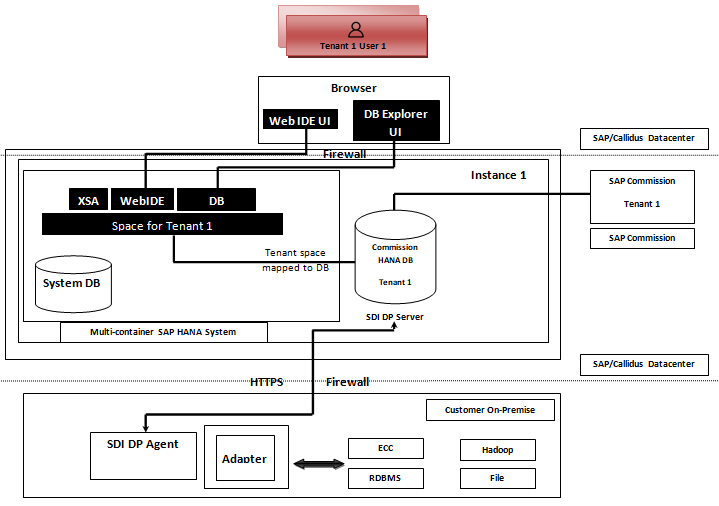
SAP packages the Smart Data Integration as a component of HANA Enterprise, which includes the following features:
- Data Provisioning Agent hosted on-premise by customers
- HANA Server (SDI Data Provisioning Server) hosted by SAP/Callidus Datacenter
What are the requirements of the SAP SDI?
SAP Smart Data Integration is an Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) tool that provides data replication features from a vast range of source systems to SAP HANA. It is inbuilt with SAP HANA. Business holders do not require any separate license for SDI.
All the data transformation processes, such as row generation, History preservation, etc., are the same as Business Object Data Services (BDOS) in SAP. But most importantly, The SAP SDI is more advantageous than the SAP data services as an ETL tool.
The following are the requirements and advantages of the SAP SDI over SAP data services:
- Business holders require a separate license for SAP Data services, but SDI is inbuilt.
- The HANA cloud includes Smart Data Quality (SDQ) with SDI. But in SAP data services, businesses require a separate license for Data Quality Transforms.
- SDI supports both real-time replication and batch replication. But BODS only supports Batch replication, i.e., scheduled replication.
What are the restrictions of the SAP SDI?
There are certain restrictions of SAP SDI that the article will discuss below:
- SAP SDI has restrictions in handling very complex and large datasets. Sometimes users face difficulties in resolving error exception that appears in SAP SDI while using SAP SDI, and finding no solution, they end up in the cleanup activities of the remote source and move on with connection rebuild.
- SAP HANA SDI DB2LogReader Adapter has restrictions with DB2 9.7 and real-time support.
- While users rebuild the connection of remote sources, it takes a lot of time because of the drooping of remote subscriptions, conducting the cleanup activity in the source system, and recreating the remote source. Also, adding up, it again puts the replications chores and starts the initial real-time data load. Thus, it consumes a long time which depends on the table size and access to the backend database.
- During the subscription process, if any subscription fails while using SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI), all other subscriptions using the same remote source will be pending till users clear the exceptions.
What are the features and benefits of SAP SDI?
Smart Data Integration (SDI) is an engine that works on the SAP HANA platform, and business holders can use it for data integration with SAP Commissions. The following are some key features of the SAP SDI:
- As we have discussed, it supports all kinds of data integration, such as Transform, Load or Extract, Bulk or batch Extract, real-time data replica, and data virtualization. SDI works on the database layer.
- It satisfies every business need by fulfilling the customer requirement by providing a web-based interface for developers to design a data integration path to meet their needs.
- SAP SDI has built-in scheduling and monitoring features. It helps to connect the customer's source data in a simplified way with several built-in connectors to many common database types.
- SDI cracks three typical challenges that every client faces while pursuing to integrate data with SAP Commissions. These are: businesses that integrate data with Commissions can often be very high in volume. Second, at almost every transformation, they need to transform the data from source systems in some way, and last is performance. SAP SDI manages these data transformations by many customers who move large amounts of data each day before executing a compensation calculation.
- SDI performs on the database layer, instead of the application layer, for handling high-volume data loads with the highest performance. It omits the chances of a volume or performance blockage on the application layer.
- Connecting multiple data sources becomes one of the most time-consuming and complex facets of configuring data integration.
- To streamline this process, Smart Data Integration provides a collection of data connectors to multiple common data sources. It comprises big data such as Hadoop, relational databases, flat files such as CSV files, Microsoft Excel, and popular social media platforms such as Twitter and LinkedIn.
Wrapping up:
Data Integration is one of the common practices for every business to flourish in the market with priority demand. With SAP Smart Data Integration, clients can improve the quality of their data across the enterprise.
SDI helps to securely transfer crucial business data to and from the Commissions application, allowing business holders easily synchronize and share data within a business community.