A set of tasks performed to achieve a specific business objective is known as a business process. BPM in business processes involves utilizing management techniques and tools to enhance task completion and value creation within these processes. Whereas, BPR is a business process where restructuring and redesigning current processes is done to achieve a significant boost in business outcomes.
Here in this article, we will learn what is BPM and BOR and the difference between BPM and BPR.
BPM vs BPR
| Concept | BPM | BPR |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business Process Management | Business Process Reengineering |
| Function | Transformative and continuous | Radical and abrupt change |
| Implementation | Short and smooth upgrade | Long-term and time-consuming |
| Change initiation | Flexible as per requirement | One primary process at a time |
| People involved | Process and People alike | BPR team with expertise from each major process units, management |
| Outcome | Improvement of business | Can have a dramatic effect on business output |
| Cultural issues | Not much of a concern | Can cause serious issues |
| Risk involved | Low | High |
| Lay-offs | Does not warrant lay-offs | Employee lay-offs are much higher as a result of process automation. |
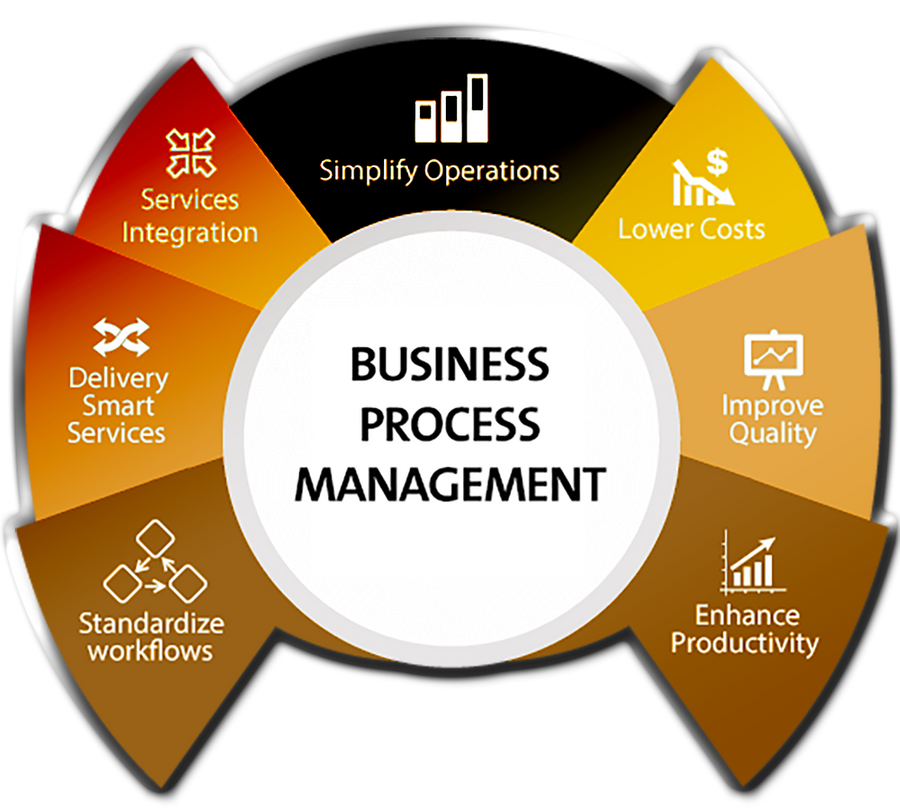
What is BPM?
BPM is a set of various management rules that govern functional roles, responsibilities, regulations, vision, goals, incentives, and business strategies. Various methodologies and tools have emerged to manage processes effectively, such as Six Sigma and lean management for continuous improvement, as well as Agile or iterative systems for gaining a competitive edge.
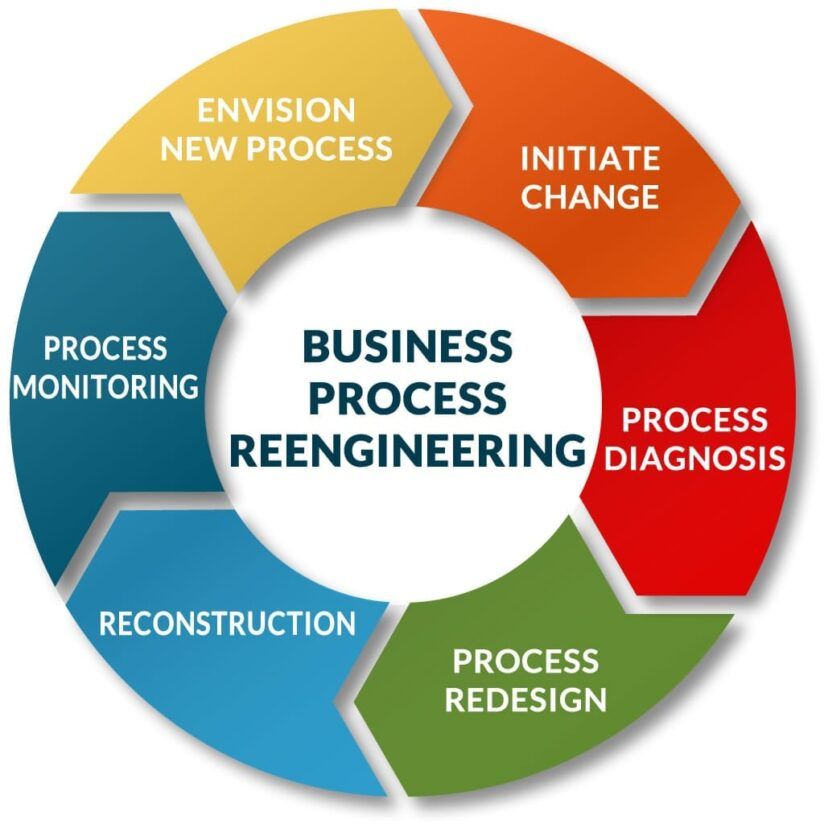
What is BPR?
Business process reengineering involves implementing radical changes to the entirety of a business process to achieve a significant leap in organizational outcomes. Information Technology plays a crucial role in this transformation by enabling the redesign of processes through IT-enabled process maps, flowcharts, and the automation of repetitive tasks.
Objectives
BPM:
- Enhancing customer satisfaction and business value.
- Facilitating continuous improvement and agility.
- Motivating employees towards achieving business goals through process management systems.
- Standardizing business processes to reduce the risk of human error.
- Simplifying and streamlining operational activities to boost business.
BPR:
- Planning for radical change by aligning business objectives with customer preferences and market trends.
- Identifying and redesigning major processes with the help of information technology.
- Revamping major process units to achieve cost reduction and cycle time improvement while enhancing quality.
- Reorganizing the structure, roles, responsibilities, and accountability of involved personnel to optimize process functions.
- Ensuring a dramatic leap in return on investment as a result of BPR.
Plan of Action
BPM:
- Design: Analyze existing processes and gather inputs from stakeholders to align processes with organizational goals.
- Model: Define enhancements to current business operations as needed.
- Execute: Pilot test new processes and automate where possible.
- Monitor: Establish performance indicators to measure performance against goals.
- Optimize: Continuously improve and reinforce process units toward business objectives.
BPR:
- Identifying Information: Gather and analyze data on existing processes.
- Analyze Data: Isolate root causes for process flaws.
- Plan Alternatives: Develop strategic transformation plans for process redesign.
Outcome
BPM:
- Real-time access to information for evaluation and improvement.
- Automatic organization of data.
- Development of technical models to enhance process units.
- Management of human resources through activity tracking and work rules.
- Traceability of existing gaps and flaws for process control.
BPR:
- Clarity on existing business processes and required change areas.
- Implementation of simplified, strategic, and efficient business processes.
- Improved quality and customer value.
- Reduced costs and cycle time.
- Maximization of return on investment.
Advantages
BPM:
- Continuous guidance for employees' decisions.
- Automatic prioritization and workflow.
- Access to process functions and control.
- Facilitation of forecasting and productivity.
- Lower costs.
BPR:
- Drastic improvement in process efficiency and communication.
- Reduction of costs and process cycle time.
- Quality improvement through clear process ownership.
- Elimination of unproductive activities and leverage of advanced technology.
- Integration of change management for sustainability.
- Optimization of return on investment (ROI).
Disadvantages
BPM:
- Limits chance for innovation due to a process-centric approach.
- A rigid workflow pattern restricts dynamic decisions.
- Lack of flexibility for employee input.
- Requires expertise for issue resolution within the processing system.
- Limited ease of communication through networks.
BPR:
- Not suitable for every business due to resource requirements.
- Time-consuming and expensive.
- Long-term outcomes rather than immediate resolutions.
- Higher resistance to change.
- Potential job layoffs due to error-free automation.