ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning)
Definition- What is ERP ?
ERP or Enterprise Resource Planning is smart business management software that allows an organization to manage and automate several business processes and backend functions. Various departments of an organization, such as finance, operations, human resources, sales and marketing, can gain benefits from the implementation of ERP. This can be incorporated in all kinds of businesses, regardless of their size and nature.
ERP consists of several modules and combines data from different sub-modules to provide strategies that go a long way in helping business development. Its implementation is extremely easy and fast. One of the main goals of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is to allow information flow in such a manner that business decisions can be completely data driven.
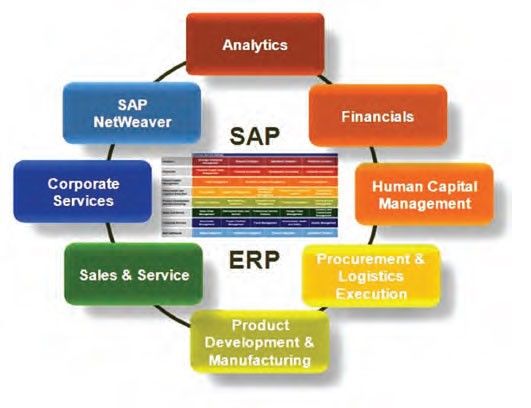
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) Improves Efficiency
ERP is responsible for driving improvements in the efficiency levels of an organization. This software:
- Helps an organization define its business processes clearly and ensures that all goals are adhered to the hilt. It provides insights that would help the management deal with any kind of deviation from pre-defined goals too. All processes that form an integral part of the supply chain need to be considered, thereby maintaining a consistency in efficiency levels throughout.
- Provides an organization with all those tools that can be utilized for maintaining higher levels of client services.
- Helps in analyzing existing orders and delivers better insights for planning the work load. This ensures that work progresses smoothly and responds well to existing working conditions. With strong ERP techniques in place, plans can be based on the insights/ forecasts predicted by the ERP software.
- Translates all the accumulated data into reliable formation from which conclusive decisions can be made. The size of the data does not bother ERP and it helps in making accurate decisions that reflect positively on business results.
- Provides stringent security to the business data. It makes sure that all the confidential data is safe and accessible only to authorized people.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP
Advantages:
- As ERP is driven by data, it is important that none of it is obsolete. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) provides real time information at all times, thus reducing the chances of redundancy and other errors.
- Integration of ERP is possible on a global scale and not just locally. It bridges the gaps caused by the differences in currency, language or culture. Additionally, it is easy to implement.
- If ERP updates need to be implemented for the entire company, then they need to be done just once, instead of going through individual departments.
- The interface is user friendly and customizable. This allows end users to state the operational structure of the product.
- Overall, the work environment is made extremely efficient for all employees.
Disadvantages:
- Though there are not many, ERP does have a few disadvantages.
- If company goals are not defined properly and if the need of ERP is not clearly stated, there exists a risk of failed implementation. To avoid this, a company has to be very clear on why and how it wants to incorporate ERP into its system.
- It may take a while to get good returns on investments.
Tutorials
- Top 10 Free Open Source ERP Software for Small Business
Managing the day to day operations of an organization is certainly not an easy task. There are so many things to be worked upon right from managing the pricing, planning for the product, finance and a ... - ICF_SYSTEM_LOGIN 402/ 403, ICF System Issue
ICF System Issue login Error, Login fails and Logon CookieSystem issues one of the following error messages and system logon fails."Logon with URL parameter not possible; logon cookie is missing& ...  SAP ERP SCM Logistics Execution System (LES) and its Functionalities
SAP ERP SCM Logistics Execution System (LES) and its Functionalities
The ERP SCM Logistics Execution System is a crucial and important component of the Supply Chain Management (SCM) system and allows the administrator to monitor, manage and control all the stages and p ...- SAP ERP PLM (Variant Configuration and its Classification)
Consistent product data, holistic processes, and an integrated document management system - that’s SAP ERP PLM - Classification and Variant Configuration for you. Presenting the results of most ... - SAP ERP Financials Assets Accounting
SAP ERP helps in integrating the multiple processes and functions of a business into one comprehensive system and provides non-duplicate and accurate support to the functional areas of: Operations Hum ... - Error: F5144 'Reconcil.acct missing in master record'
The SAP error F5144 - "Reconcil. acct missing in master record" occurs when a reconciliation account is not assigned to a customer or vendor master record. The reconciliation account is a ke ... - SAP SCM Customer & Vendor Management Features and Benefits
The popular SAP enhancement package 4 that offers adequate support for SAP ERP 6.0’s support package 9 (relating to SCM), the ‘Customer and Vendor Master Data Integration’ sub module ... - SAPF190 displays differences between indexes and balances/transaction figures
SAPF190 displays differences between indexes and balances/transaction figures a) for G/L accounts In the majority of the cases where an error occurs, the total of the indexes on the debit or cre ...  SAP ERP Finance and Controlling Solutions.
SAP ERP Finance and Controlling Solutions.
What is SAP ERP Financials? SAP ERP Financials provides modular applications that enable organisations to tailor SAP solutions to their specific business needs. These applications cover core accoun ...- ERP and SAP ME Integration via POIT & POIM T-codes
Is it possible to use the current integration between ERP and SAP ME via the transactions POIT and POIM incase the improved integration is activated? SOLUTION If the user has switched on the imp ... - ERP with an SAP ME
What makes the improved integration between ERP and SAP ME? If the improved integration between ERP and ME is active, you can use the following improvements: Production orders, planned orders ...