GST (Goods And Service Tax)
Definition or Meaning- What is GST?
Full form or GST stands for (Goods and Services Tax), GST is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. GST replaced many of the existing taxes that were operational in the different Indian states. GST was passed at the Parliament on 29th March 2017. The tax was officially launched on 1st July 2017. This is an indirect tax that is known as a multi-stage, destination-based and comprehensive. It is implemented on the supply of goods and services.
The tax became famous for replacing many of the existing taxes that were operational in the different Indian states. The GST council that consists of central and state finance ministers governs all these rules and regulations that have been implemented.
Why GST was Introduced (Goods and Services Tax)?
GST was applied to improve the economies of the states and the overall country. Here the tax will be levied at every point of the sale and so GST is called multi-staged. This will be refunded to all the parties at every stage of the production of a certain good. GST is considered a destination based as the tax is collected from the destination of consumption and not the origin.
For example, consider the goods originate in West Bengal and are sold to consumers in Gujarat. As GST is collected from the point of consumption, the entire revenue of the tax will go to Gujarat and not Bengal.
GST is levied on the value additions that are added during each stage of the manufacturing process of a product. For example, a biscuit manufacturer purchases wheat, flour, and sugar. The value of these ingredients increases when they are mixed and converted into a biscuit. This value is increased when the manufacturer sells the biscuits to a warehousing agent who stores them.
The agent sells these to a retailer and the value increases again. The goods are finally sold to the customer.
Components of GST
The different components of GST are:
- CGST – This is GST collected by the central government on the sales that happen within the state.
- SGST - This is GST collected by the state government on the sales that happen within the state.
- IGST - This is GST collected by the central government on the sales that happen between two states.

History of GST
In 1954 France became the first country to implement GST tax regime in their country followed by Germany, Italy, South Korea, UK, Japan, Canada and Australia and many more. Today almost 160 country have implemented GST in their respective countries.
Formula to Calculate GST
In order to calculate GST we can use the formula below:
GST Amount = ( Original Cost * GST% ) / 100
What are the Benefits of GST?
The different advantages of GST are as follows:
- GST is comprehensive and aims to bring all types of taxes under one umbrella. Therefore, different indirect taxes such as VAT, Excise, CAD, CST, SAD, and Service tax are removed
- As the tax burden is lowered, the manufacturing costs are also lowered. This makes many products cheaper
- The demand and consumption of goods are increased
- The Composition scheme will help many small scale companies to lower their taxes
- Many provisions for the e-commerce sector have helped them improve their businesses and the goods can be transferred easily
- The unorganized sector has been regulated by GST
Conclusion
Through GST, many central and state taxes are integrated into one that will make taxation simple for all. Many small scale and large-scale industries are benefited as a result. This is a huge step towards the betterment of the country’s economy.
Tutorials
 Configure STO (Stock Transfer Order) process for GST
Configure STO (Stock Transfer Order) process for GST
This tutorial explains the configuration process of setting up STO (Stock Transfer Order) process for GST India.Configure Plant as a VendorThe plant that has to be sent in the Stock Transfer process s ... GST IN Procurement Configuration in SAP
GST IN Procurement Configuration in SAP
Configuration for Procurement Condition table maintenance Executing the t-code M/03 Source combination: Country/Region/PlntRegion/GST Class./Tax ind./Ctrl code Technical View: ... Official Document Numbering (ODN) Configuration for GSTIN
Official Document Numbering (ODN) Configuration for GSTIN
How to Configure Official Document Numbering (ODN)?This tutorial explains how to configure Official Document Numbering (ODN) for GST India.Document Classes Maintenance First execute the t-code SM30 No ... Reverse Charge Tax Configuration Mechanism for GST IN
Reverse Charge Tax Configuration Mechanism for GST IN
Reverse Charge Tax Configuration Scenario For GST IndiaConfiguration for ProcurementCondition types1.Deductible reverse charge condition typesBelow are the 4 reference condition types delivered in pre ... GST Vendor classification issue in FV11
GST Vendor classification issue in FV11
Error: Fill in all required entry fieldsGST vendor classification does not accept any blank value and gives an error 'Fill in all required entry fields' while maintaining condition records in ... SAP offers ASP for GST India
SAP offers ASP for GST India
The GST India administration will have two major players: GST Suvidha Provider (GSP) Application Service Provider (ASP)Read more here Indian Tax Procedure Migration from TAXINJ to TAXINNThe follo ... Import Process For GST India
Import Process For GST India
What are the steps involved in GST India Imports Scenario???The process involved in GST import scenario are: First, create a purchase order, Purchase Order must always consist of basic custom duty con ...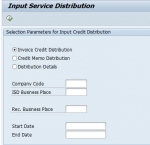 Input Service Distribution (ISD) Process GSTIN
Input Service Distribution (ISD) Process GSTIN
What is the process Involved in Input Service Distribution (ISD) for GST India?SOLUTIONBelow are the steps involved in Input Service Distribution (ISD) Process: First, execute the transaction cod ... Tax Configuration (Withholding TDS) for GSTIN
Tax Configuration (Withholding TDS) for GSTIN
Steps to create official withholding tax keys Please follow the steps below: Execute t-code SPRO in SAP command field Next, click the SAP Reference IMG button Now navigate to the f ... Tax Indicator (TAXIM) Fields for GST IN
Tax Indicator (TAXIM) Fields for GST IN
What is the Tax Indicator fields used for GST India in SAP standard system?SOLUTION1) SAP has allotted tax indicators, 0,1,2 and 3 as the part of the design.2) As for now there are four possibilities ... External Service Management for SAP GST MM India
External Service Management for SAP GST MM India
Taxes activated for Individual service line item level:1.Navigate to SPRO Path in order to maintain Taxes at service line item level.IMG->Material Management->External Service Management->Tax ... Data Dictionary Activities
Data Dictionary Activities
Changes to Existing Domain First execute transaction SE11 and give domain name as ‘J_1ICONDNAME1’ and click on ‘Change’ Now in value range tab add below values at the ... Extend Pricing Structures KOMP and KOMG
Extend Pricing Structures KOMP and KOMG
How to extend pricing structure KOMP and KOMG?SOLUTIONExtending Pricing Structure KOMP Please follow the steps below for extending the pricing structure of KOMP:1. First, go to transaction code S ... Tax Procedure Configuration for Sales and Distribution
Tax Procedure Configuration for Sales and Distribution
Maintaining Condition TableExecute the transaction V/03 Source Combination : Country/ PlntRegion/ TaxCl1Cust/ TaxCl.Mat/Region/ Ctrl codeSource combination: PlntRegion/Region/TaxCl1Cust/MaterialS ... Post Implementation Steps for STO (Stock Transfer Order) GSTIN
Post Implementation Steps for STO (Stock Transfer Order) GSTIN
STO (Stock Transfer Order) Post Implementation Steps for GST IndiaCreate PF status J_1IG_STO_STATPlease follow the step below in order to create PF status J_1IG_STO_STAT First please execute t-code SE ... BADI INVOICE_UPDATE Implementation GSTIN
BADI INVOICE_UPDATE Implementation GSTIN
Create Implementation For BADI INVOICE_UPDATE in GST IndiaPlease follow the step below in order to create an implementation for BAdI INVOICE_UPDATE:Step 1) First Execute t-code SE18 and then ente ... BADI_SD_SALES_ITEM GST Implementation
BADI_SD_SALES_ITEM GST Implementation
1.First, execute transaction code SE18 and then enter the BADI ‘BADI_SD_SALES_ITEM’ and select ‘Display’ button2.Now please click on ‘Implementation’ and then selec ...- Vendor Down Payment GSTIN
How to clear line for Vendor down payment for GST India?Following are the steps involved in for Vendors Down payment: First, configure Vendor down payment. Now execute the t-code F-48. Now the GST wil ... - Customer Down Payment GSTIN
How to clear line for Customer down payments for GST India?Following are the steps involved in for Customers Down payment: First, configure customer down payment. Now execute the t-code F.29. Now the ...  Create Smart Form Invoice For GSTIN
Create Smart Form Invoice For GSTIN
How to create Smart Form for GST (Goods and Services Tax) India?SOLUTIONPlease follow the steps below in order to create Smart Form for GST India First execute the t-code ‘SMARTFORMS’. The ...