Graphs are the most efficient way to visualize data models and relationships between datasets. Graphs can seamlessly represent data that are too numerous or complex to be characterized decently in the text and occupy less space.
The SAP Graph is a new user-friendly API for SAP's Integrated Intelligent Suite. It allows users to expose all their business data in a semantically connected data Graph format. Users can access this through a single unified and powerful API.
This article emphasizes the SAP Graph as a new business technology platform for SAP customers.
What is SAP Graph?
SAP Graph or SAP Data Graph, also called Business Data Graph, is a new unified, user-friendly, and consolidated API. Developers use SAP Graph to create applications that access an affiliated Business Data Graph of SAP-managed data, nevertheless of where their data resides.
This API allows presenting their business data through a connected and integrated Graph. It means developers can seamlessly navigate and access the data they need, regardless of the location.
In SAP, the Business Data Graph acts as a middleware that provides access to data in the customer-configured landscape on behalf of its users. But, most importantly, the SAP Graph does not save or cache any data.
Developers can configure it in an SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP). SAP Graph is a standalone service on the SAP BTP. The Graph functionality in SAP is a characteristic of API Management.
Developers can use it in addition to the other attributes or use SAP Graph as an "unmanaged" API within their API Management configuration. The central purpose of Graphs is to create a data abstraction of the developer's landscape in the form of a navigatable Data Graph.
They can then integrate its application with other policies.
Functions of SAP Graphs
The Graph is the latest, extendable, innovative tool of API Management within the SAP Integration Suite. SAP introduced the integration of this new and more advanced release of SAP Graph into API Management at SAP TechEd 2022. The new functions of the SAP Graph are as follows:
- The SAP Graphs provide a configuration UI to build Business Data Graphs. It is an extension of the new Integration Suite configuration UI, i.e., having capabilities for extending the out-of-the-box Graph data model.
- SAP Graph Navigator for enterprise edition is a tool that helps in exploring and testing out queries on the developer's own configured Business Data Graphs
- SAP Graphs provide GraphQL support over and above OData v4
What does SAP Graph address?
Businesses are growing more data-centric, which indicates an increasing demand for more advanced and productive systems. SAP customers want to become more Intelligent Enterprises in the matter of handling complex and large data.
For this, SAP uses its ERP solution to manage business data which allows organizing and storing complex scattered data of companies in a single location. ERP also exerts a level of automation that allows staff members in the overall business to monitor shared data without accessing manual records.
But the need for more complex requirements compelled SAP to augment its ERP-centric business suite with substantial additional functions via the acquisition of cloud solutions.
These suites are SAP Concur, SAP SuccessFactors, and SAP Ariba.
This integration of the intelligent portfolios from SAP allowed the business suite with all the major business processes, spanning all the interface functions.
All these SAP advanced solutions, expanded role, and diversity of solutions has introduced some new complexities. Many of the suite's products from SAP include individual stack, which overlaps data models, various APIs, and heterogeneous networks.
More significantly, the growing complexity is not always well hidden from SAP's customers. Accessing SAP-managed data has become more intricate with these complexities. Thus, these data should get federated across hybrid networks of on-premise and cloud solutions with diverse security protocols, replication systems, and numerous master data copies.
SAP Graph addresses these complexities and brings the most advanced and efficient business solution. It is a unified and consolidated API for SAP. This ultimate solution of the SAP manages these run-away API complexities by integrating challenges.
It provides developers with a single merged and unified view of all their business data, crystallizing the data models of data sources such as SAP Sales Cloud, SAP S/4HANA, and SAP SuccessFactors into a single platform. This unified and connected data model represents all the data in a single landscape, i.e., the Business Data Graph.
Explore the SAP Graph on the SAP Navigator
SAP documented the Graph API in a new SAP Graph Navigator. It provides one connection to all the business data, providing a precise specification of all the entities in the Business Data Graph. These entities include attributes and associations, including interactive examples.
Here is an example of a Graph Navigator application with over fifteen thousand entities grouped by data source:
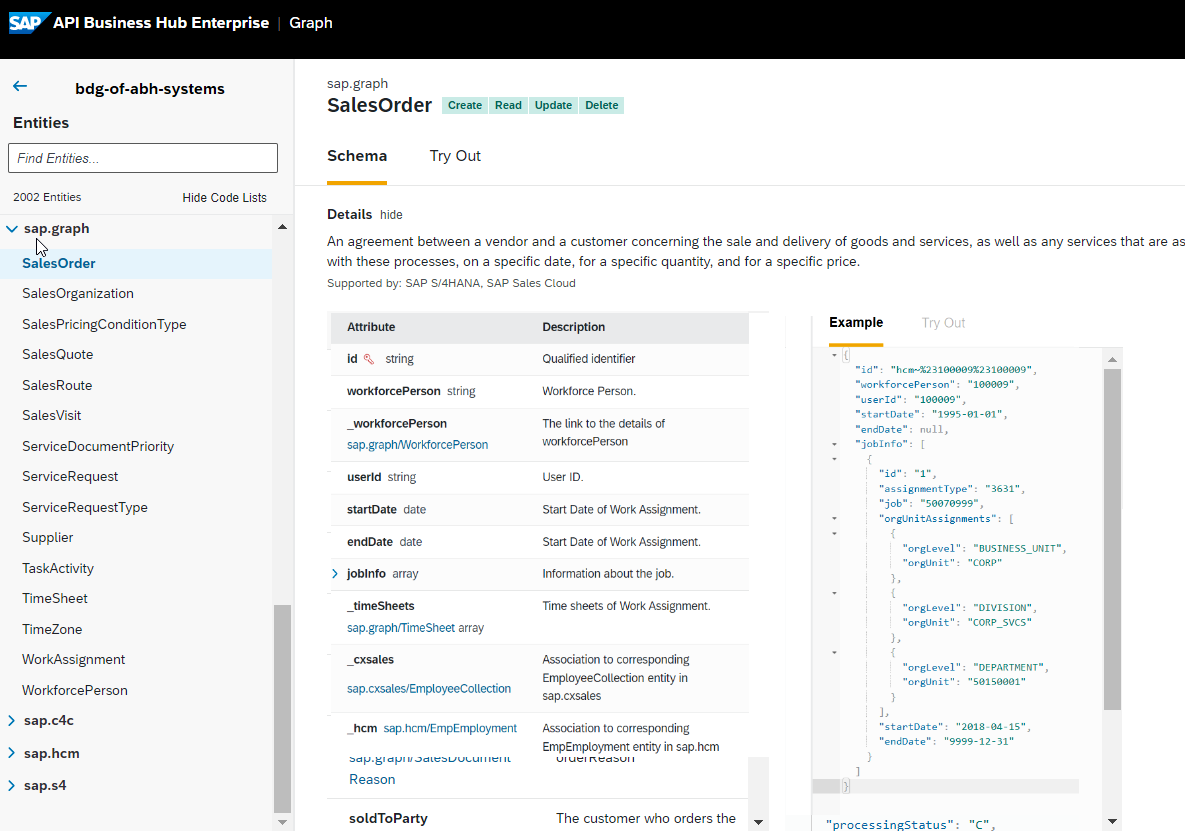
These entities with attributes allow developers to extend the information available in a unified entity with system-specific attributes. It makes the Business Data Graph more effective, connected, and negotiable for the overall enterprise infrastructure.
Advantages of Using SAP Graph
The following are the advantages of using SAP Graph for SAP-managed data, which simplifies faster innovation for SAP customers:
- It allows developers to create applications to primarily access SAP data from multiple lines of business (LOB) systems. For instance: SAP S/4HANA Cloud, SAP S/4HANA, and SAP Success Factors.
- SAP Graph allows companies to downsize the expense and complexity of building and deploying reusable extension applications.
- The term "Graph" determines the connections between data objects, allowing easy access to monitor shared data without accessing manual records.
- SAP Graphs assist developers in building extensions on top of solutions. These help the customers take maximum advantage of the spectacular breadth of SAP business applications as developers navigate to SAP S/4HANA and the whole intelligent suite.
Security of SAP Graph
The demand for SAP-managed data is exponentially growing with the increasing market of distributed systems for handling business data. It compels the growth of robust security for companies that use SAP solutions.
SAP Graph allows SAP customers to ensure their SAP solution supports their business requirements without permitting unauthorized access to essential information. The security model of the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) guarantees the security of the Business Data Graph.
The leading principle of this SAP system is the formation of isolated domains, which creates a strict security detachment of different customers, as executed through SAP BTP subaccounts. The SAP BTP security principles and services govern the identification, role assignment, and authorization.
Conclusion
The rising demand for business data and increasing complexities take effective SAP solutions like SAP Graphs or Business Data Graphs to a new vertical. It is the best form of managing business data and provides a single connected and unified view of all the business data.
This SAP article highlights the importance of SAP Graphs for companies with robust security models. Exploring all these ideas will undoubtedly help get your hands on the right solution you want to manage business data efficiently.