SAP SD (Sales and Distribution)
Most companies offer some kind of service or product to their customers. Either way, sales, and distribution are the aspects that run their business. These companies need to constantly assess their sales strategies and procedures. This is important for reaching out to more customers and markets.
In this tech-driven era, companies choose ERP software for handling their sales and distribution activities. For this, the SAP Sales and Distribution module are one of the best in the market. This is an ERP module developed by SAP that can handle all customer and distribution data in organizations. It can also work with other useful modules such as SAP Financial Accounting, Materials Management, and Production Planning.
Furthermore, SAP SD automates tasks such as packing, delivery, order processing, and shipping of products. In this post, we will discuss all the interesting features of SAP SD.
What is SAP SD?
Full form or SAP SD stands for (Sales and Distribution), is a core module in SAP ERP Central Component (ECC). This software solution handles all the tasks in the sales and distribution cycle. Right from raising a quotation, purchase, and billing the sale – SAP SD oversees it all. First, SAP SD generates a sales quote. Then, the customers place an order for a product or service. The goods will be picked up from a warehouse and will be sent to the customer. An invoice is prepared and the payment is received from the customer.
All these steps generate a lot of transaction data. The SAP SD module stores and processes all this data.
SAP SD is designed to carry out these important functions in any company –
.jpg)
- Customer Master and Material Master Data– It collects and maintains databases of client products, orders, shipping details, addresses, and preferences. The software handles all related data about the sales and distribution department.
- Sales– Aspects such as making sales forecasts, developing marketing strategies, and creating ads, are handled by SAP SD.
- Pricing– It maintains pricing information, price lists, product pricing, and associated data.
- Billing and Invoice– SAP SD generates invoices, bills, statements for product deliveries and orders.
- Credit Management– It manages the credit issues of the customers and settles credit limits.
- Availability Check– It keeps track of the company’s inventory of products. Moreover, it handles the placement of orders when goods run out of stock.
- Shipping and transportation– SD even takes care of order delivery processing, shipping, and transportation.
- Output Determination– It handles all the communicative documents such as printouts, emails, telexes, faxes, or EDI that is exchanged between two companies.
- Batch and serial number management– This software manages and issues all product serial numbers.
- Foreign Trade– Tackles all the information related to trading. This includes imported and exported products.
Component of SAP SD
These core components of SAP SD are –
- SAP-SD-MD: Master Data
- SAP-SD-BF: Basic Functions
- SAP-SD-SLS: Sales
- SAP-SD-SHP: Shipping
- SAP-SD-TBA: Transportation
- SAP-SD-FTT: Foreign Trade
- SAP-SD-BIL: Billing
- SAP-SD-CAS: Sales Support
SAP-SD-MD (Master Data)
This data tracks all the information about each transaction taking place. The sales and distribution master data includes the following –
- Material master data
- Customer master data
- Output records
- Pricing conditions record
It also handles credit management and order processing data.
SAP-SD-BF (Basic Functions)
This component takes care of all the basic functions in sales and distribution. It calculates and processes the pricing amount required for a specific sale. SAP SD BF also processes the resultant output of the sale.
SAP-SD-SLS (Sales)
This component handles all the particulars of the sales that take place in the company. Storing product details, customer information, pricing data, customer feedback, and other related sales processes are tackled by SAP SD SLS.
SAP-SD-TBA (Transportation)
SAP SD TBA is a component that works along with the SAP shipping module. A company can manually deliver a product or use a courier to ship it. No matter what the mode of transportation is, the information is tracked and processed here.
SAP-SD-SHP (Shipping)
Creating high-quality products and services for the customers is a job half done. It has to be delivered to them properly. For the various forms of delivery and shipping, the SAP SD SHP component tracks all the associated data. It tracks every delivery. The complete process, from shipping to product delivery or return, is recorded by the component.
SAP-SD-FTT (Foreign Trade)
This component stores and processes data about the company’s foreign trade. All product imports and exports are tracked by them. The component is great for organizations that conduct business worldwide.
SAP-SD-BIL (Billing)
Perhaps the most important part of any transaction is billing. A customer can pay for the products in cash, credit card, or via PayPal. So, this billing information is important for future reference. Thus, this component is used to track every billing detail.
SAP-SD-CAS (Sales Support)
A customer will interact with the sales team during the purchase of a product. During this process, a lot of data will be generated. The SAP SD CAS component is used for storing the sales support data between the company and the customers.
SAP SD Enterprise Structure
SAP SD enterprise structure displays the structure of an organization in the SAP R/3 system. The sales and distribution module represents consist of the following organizational units –
i) CLIENT
A client is an independent organizational or legal unit. It is also considered a self-contained technical unit. These are used in storing generic tables and data for various organizational structures. When it comes to the enterprise structure, the client sits right at the top.
You can assign unique company codes to a particular client.
ii) COMPANY CODE
This is an organizational unit that is created in the SAP FI module. It represents an independent organization. This being a legal entity, all balance sheets and profit/loss statements are stored at the Company Code level. Moreover, different company codes can be assigned to a client.
Various Company Code under the same client can have the same account charts. So, at the company code level, many companies maintain their books of accounts.
iii) SALES ORGANIZATION
Sales Organization in the SAP SD module is at the top level of the organizational structure. This is used for developing and monitoring sales strategies. If the company’s customers have any complaints or queries about their products/ services, it is handled at the sales organization level. All the sales reporting is also done at this level.
Furthermore, the sales and distribution documents are assigned at this level.
iv) DISTRIBUTION CHANNEL
This is a strategy for entering a particular market where you want to sell products or services. A distribution channel will help you to reach out and connect to your target users. Within a sales organization, a customer can be served via one or more distribution channels.
Developing master data, important sales documents, billing documents, and business lists are done through the Distribution channel.
v) DIVISION
A division consists of a group of products or services having similar characteristics. This also represents the product line of any business. Different divisions can share the same master data. Also, this master data can vary from one division to another.
A division can be used for creating a delivery worklist and also as a selection criterion.
vi) SALES OFFICE
Companies set up different sales offices apart from their headquarters for carrying out sales operations. These offices act as a bridge between the head office, sales department, and the end-user.
All sales reporting is carried out within the sales offices for analyzing sales performance.
vii) SALES GROUP
A sales group consists of employees under the sales office. Being a subset of the sales offices, this group carries out all the internal sales tasks.
One sales group can be assigned to more than one sales office.
viii) PLANT
You can consider a plant as a distribution center. This is the place from where goods and services are dispatched. All the stocks are kept here.
ix) STORAGE LOCATION
This is a location where the company’s stock is kept. It is assigned to a particular plant and falls under the logistics unit.
x) SHIPPING POINT
A shipping point is assigned to a plant. The place is used for shipping goods to the customer. Based on the dispatching activities, a plant may have multiple shipping points.
Characteristics of SAP SD
The important characteristics of SAP SD are –
- Helps in determining the prices of goods and services. Conditions such as discounts and rebates are also offered to the customer
- Determines customer details as per conditions
- Helps in generating bills, transactions, and records of sales
- Assists companies in developing business processes for billing and selling of products
- SD’s real-time currency rate database helps in converting various international currencies
- Handle complex pricing schemes and rebate processing for customers
- The Sales Information System enables simple sales reporting by sorting and storing data
- Any user can enter basic order details into the software. They can find out information regarding levels of the order and schedule line information
- Makes batch processing of orders, shipments, and sales documents easier
- You can use this software to check the availability of goods in the company’s inventory
- Offers automatic credit check and simple credit check. This helps in managing the credit limits of customers
Conclusion
SAP SD has been a boon for many companies who wanted to enhance their sales and distribution. As the software offers real-time data on customers and inventories, organizations can assess their sales performance. The software assists in determining key performance indicators. This, in turn, helps them measure their return on investment. It also helps in analyzing the performances of the sales teams.
Overall, SAP SD is a comprehensive solution for any company’s sales department.
Tutorials
 PGI (Post Good Issue)
PGI (Post Good Issue)
What is PGI Means? PGI stands for Post Good Issue, PGI stands for Post Good Issue. is a process that confirms the delivery of goods to a customer or to another location within the company's pre ... User Exits in Billing Document
User Exits in Billing Document
Additional User Exits in Billing DocumentFill in the fields in VBRK/VBRP tables - USEREXIT_FILL_VBRK_VBRP in the include RV60AFZC.Determine the number range for internal document number - USEREXIT_NUM ... Incoterms and How to Configure Incoterms?
Incoterms and How to Configure Incoterms?
What are Incoterms? Incoterms is an international commercial term that defines the terms of sale and the passing of risks for the import and export of merchandise. Incoterms play an important role ...- User Exits available for SAP SD (Sales and Distribution)
To find out various User Exits available for SD applications go through this path:SPRO > IMG > Sales and Distribution > System Modifications > User exits. Sales related exitsCust ...  Movement Type Concept
Movement Type Concept
What Is a Movement Type? When you enter a goods movement in the system, you must enter a movement type to differentiate between the various goods movements. A movement type is a three-digit identif ... SAP IS-Retail Overview
SAP IS-Retail Overview
The world of retail is extremely dynamic. With ever-changing market trends and customer demands, retail companies always have to be equipped to handle them. They have to alter their business processes ... SD Transaction Codes (Sales and Distribution)
SD Transaction Codes (Sales and Distribution)
List of all the important transaction codes used in SAP SD is below: T-code Description SPRO Enterprise IMG VS00 Master data V ...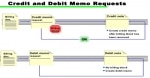 Define Debit note and Credit note.
Define Debit note and Credit note.
Debit note and Credit note Definition, Function, Format Definition: A Credit note is a monetary document used to exchange for goods of equal value, issued by a seller to a buyer.The credit ... Define Account Assignment Group
Define Account Assignment Group
Field found in Material Master Sales Organization 2. To define the General Ledger Posting:- IMG -> Sales and Distribution -> Account Assignment/Costing -> Revenue Account Determination ... Availability Check Configuration in SAP SD
Availability Check Configuration in SAP SD
What is Availability Check and How to Configure it?When we create a sales order, there are several basic functions which are executed automatically for the dynamic order management . among these basic ... Invoice Splitting Criteria in Billing Document
Invoice Splitting Criteria in Billing Document
From a number of deliveries or sales orders more than one billing document is created. As a rule, the system combines into one billing document all transactions for the same customer, default billing ... Difference between User Exit and Routines
Difference between User Exit and Routines
Routines vs User Exit in SAPUser exitIn this step, you can implement the user exits listed below.You should carry out this step only if both of the followings apply: The SAP standard processes do ...- Delivery Split during Delivery Creation
To understand the split reasons displayed in the log, you must know the basic approach of the system during the creation of deliveries:When you create the delivery, an interim delivery header with the ... - Order to Cash Cycle
The SAP Order to Cash (OTC) Process is a critical business process that enables organizations to efficiently manage their sales operations from order creation to payment receipt. It involves multiple ... - How to Create and Process Rebate Agreement?
Following explains how to create a rebate agreement, test it using a sales order and billing it. Then settling it partially or fully using a rebate credit memo. Please use the basic procedure and twea ... - SAP SD (Sales and Distribution) Certification Cost and Course Duration in India
The course provides live training using real world scenarios. The cost of the course depends on the time duration and the institute. Some institutes offers 25 hrs duration for 25000/- to 3 lakhs for 3 ... 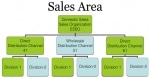 Difference between Sales Area and Sales Organization
Difference between Sales Area and Sales Organization
Sales Area vs Sales OrganizationWhen you're talking about a company, based on which thing should we take?Is it different company codes for different locations or is it based on the product group?S ...- Logistics Information System (LIS) in SAP
Answer: LIS stands for Logistics Information System. In SAP, the logistics information system is a combination of the following systems. Sales Information System Purchasing Information System Inventor ... - SAP SD Configuration Step by Step Guide
This tutorial explains SAP SD Configuration Step by Step Guide which includes topics such as Creating Sales Relevent Organisation Units, Assigning Organisational Units, Creating Master Data, Sales Ord ... 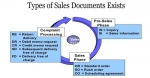 Types of Sales Documents Exists
Types of Sales Documents Exists
How many types of Sales Documents Exists?Sales document can have many different document type. Each document type has its own usage.Some commonly used document type are:- OR - Standard Order RE - Retu ...