What is SAP Profile?
SAP profiles are configuration files that contain instance setup information. SAP profiles are created during the installation of an SAP system and are stored in the system's file system, not the operating system's file system. These profiles contain a set of parameters that specify how the SAP system or instance should operate, such as database access, memory usage, and network connectivity.
Each SAP instance can have multiple profiles, and each profile has a unique name and set of parameters. The parameters in the profiles can be edited using the Profile Generator tool or the SAP Management Console.
Storage Location of SAP Profiles
The default location for SAP profiles on a Unix or Linux-based SAP server is /usr/sap/<SID>/SYS/profile, where <SID>is the unique system identifier for the SAP instance. On a Windows-based SAP server, the profiles are typically stored in the %SYSTEMDRIVE%\usr\sap<SID>\SYS\profile directory.
Each profile file has a unique name and is stored with the .pf file extension. For example, the default profile for an SAP instance is stored in a file named DEFAULT.PFL.
The SAP profiles stored in the profile directory contain various parameters that define the behavior of the SAP system or instance, including system and client settings, database connection information, and other configuration details. These parameters can be edited using the SAP Profile Generator tool or directly in the profile file using a text editor.
The storage directory for SAP profiles is an important location for SAP system administrators, as it contains the configuration information necessary to manage and customize the behavior of the SAP system.
Importance of SAP profile
1) System configuration
SAP profiles contain a set of configuration parameters that define how the SAP system or instance should operate. These parameters control various aspects of the system's functionality, such as memory usage, database access, network connectivity, and other settings. SAP profiles provide system administrators with a centralized location for managing the configuration of the SAP system.
2) Customization
SAP profiles allow system administrators to customize the behavior of the SAP system to meet the specific needs of their organization. By editing the parameters in the profiles, administrators can configure the system to optimize performance, allocate resources, and meet other operational requirements.
3) User-specific settings
SAP profiles can also contain user-specific settings, such as language preferences, keyboard layouts, and other user preferences. This allows system administrators to customize the user experience for different users or groups of users.
4) System-wide settings
SAP profiles can also contain system-wide settings that apply to all SAP instances on a particular server or cluster. These settings can be used to manage the overall performance and behavior of the SAP system.
Parameter files defined in SAP profile
These parameter files are used by the SAP system to determine how it should behave and operate. The following are the types of parameter files defined in SAP profiles:
-
Instance profile file: This file contains configuration parameters specific to a particular SAP instance. It defines the parameters that are unique to the instance, such as the instance number, host name, and system ID.
-
Start profile file: This file contains configuration parameters used when starting an SAP instance. It specifies the size of memory buffers or other performance-related settings that are required when starting the system.
-
Default profile file: This file contains configuration parameters used as a default when no other profile file is specified. It defines the default behavior of the SAP system or component.
-
Global profile file: This file contains configuration parameters that are applied to all SAP instances on a particular server or cluster. These settings can be used to manage the overall performance and behavior of the SAP system.
-
Database profile file: This file contains configuration parameters used to connect to the database used by the SAP system.
-
Transport profile file: This file contains configuration parameters used to manage the transport system in the SAP system.
-
Security profile file: This file contains configuration parameters used to manage the security settings in the SAP system, such as user authentication and authorization.
How to Create New SAP Profile?
Please follow the steps below to create a new profile
Execute t-code RZ10 SAP command field.
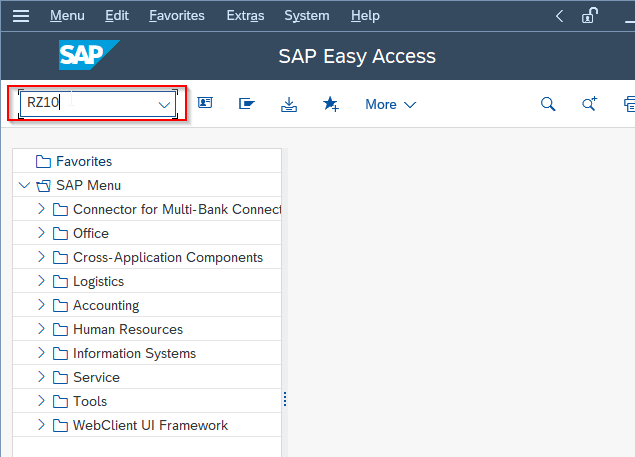
On the screen, select the profile that you want to use as a template for the new profile. You can choose the default profile or any other existing profile that you want to copy.
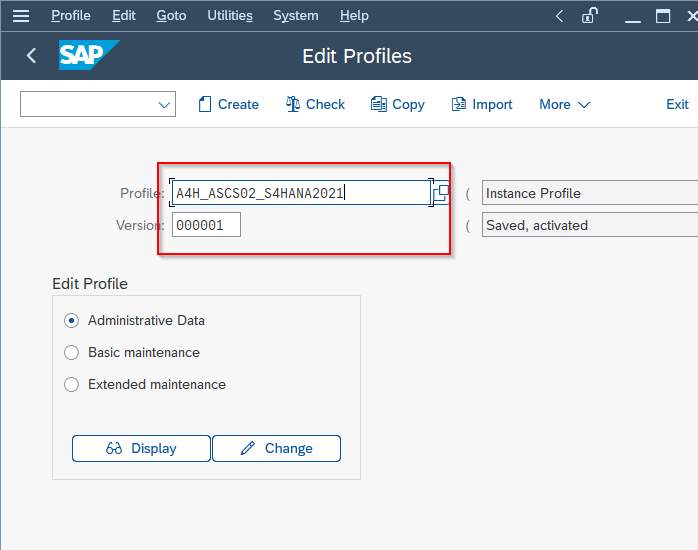
Now click the Copy button to create a copy of the selected profile.
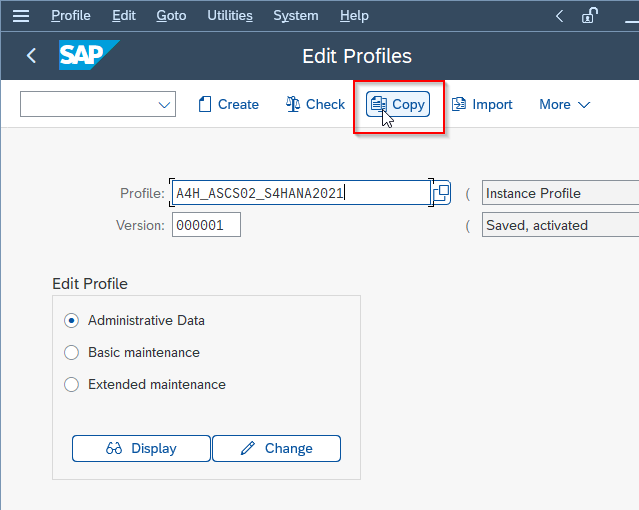
In the Copy Profile window, enter a name for the new profile and click the Copy button to create a new profile.
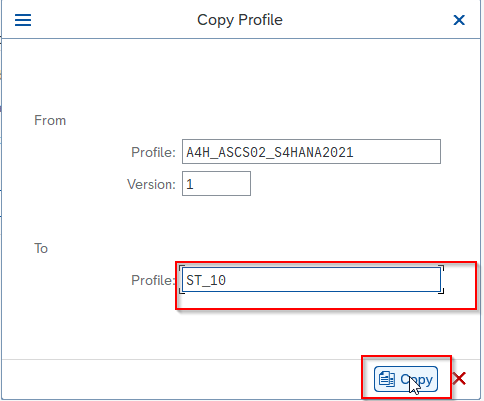
The system will generate a new profile file with the specified name and type.
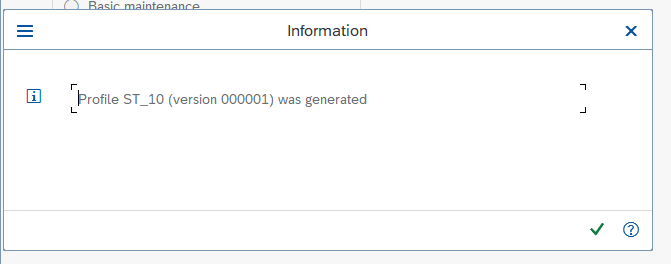
Next, select the newly created profile and click the Change button to open the Profile Management screen.
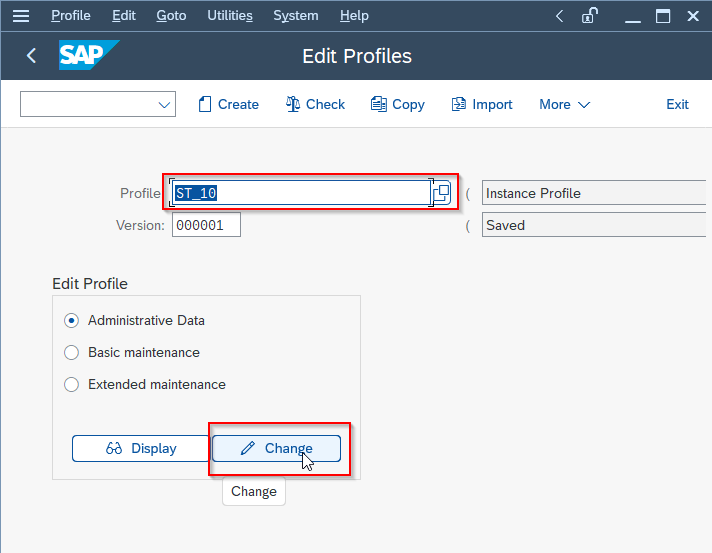
In the Profile Management Data screen, you can modify the parameters in the profile as per your requirement. You can add new parameters, change the values of existing parameters, or delete parameters that are no longer required.
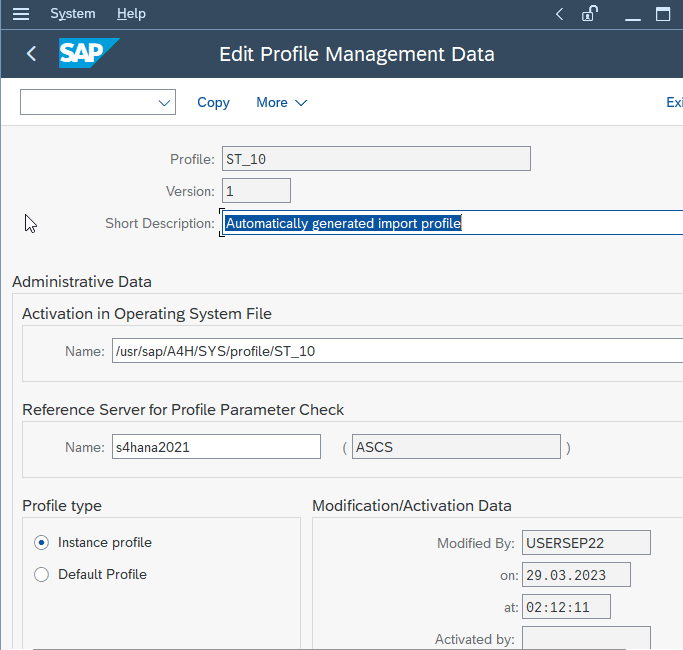
Once you have made the necessary changes to the profile, click the Save button to save the changes.
Finally, click the Activate button to activate the new profile. The system will generate a message indicating that the profile has been activated.