Scope of Financial supply chain management
- Financial supply chain management (FSCM) is an integrated approach to provide better visibility and control over all cash-related processes.
- Better predictability of cash flow,
- Reduction of Working capital.
- Reduction of operating expenses and end-to-end integration of business processes.
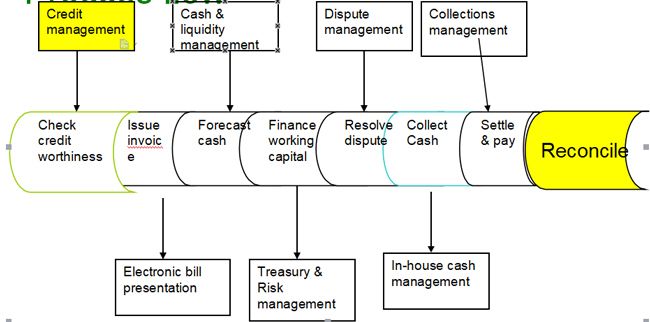
Financial supply chain management
Process flow
SAP Treasury and Risk Management (TRM)
- SAP Treasury and Risk Management is a series of solutions that are geared towards analyzing and optimizing business processes in the finance area of a company.
- Integration
- SAP Treasury and Risk Management is an integrated solution, in which the various components are closely linked.
The financial transaction managed in the Transaction Manager can be
Components of Treasury
- Business partner
- Basic functions
- Transaction manger
- Market risk analyzer
- Credit Risk analyzer
- Portfolio Analyzer (FIN-FSCM-TRM-PA)
SAP Treasury and Risk Management (TRM)
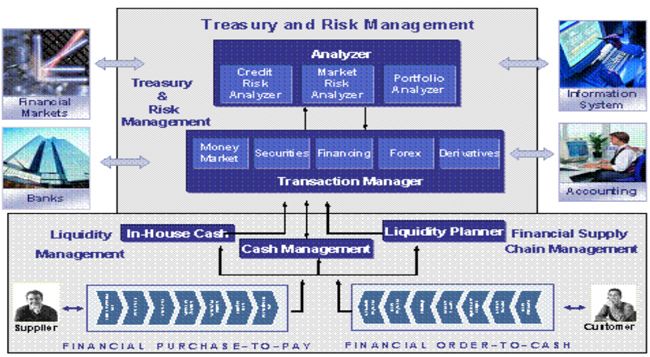
Transaction Manager
- The Transaction Manager is a powerful instrument that executes efficient liquidity, portfolio and risk management. You have the option of carrying out liquidity and risk analysis in the Transaction Manager. Based on these analyses and the current conditions on the financial markets, you can make decisions about future investments and borrowings.
- The Transaction Manager:
- Helps you manage your financial transactions and positions. This involves trading, back office, and the connection to Financial Accounting.
- Helps you utilize existing rationalization and enables you to automate typical processes.
- Provides flexible reporting and evaluation.
Features of Transaction Manager
- The Transaction Manager helps you realize the following corporate goals:
- Financial services for affiliated group companies.
- Activities on financial markets for investing liquid funds.
- Financing short-term and long-term investment projects.
- Hedging potential or existing risks.
Components in the Transaction Manager
- Money market
- Foreign Exchange
- Derivatives
- Securities
Product types in the money market
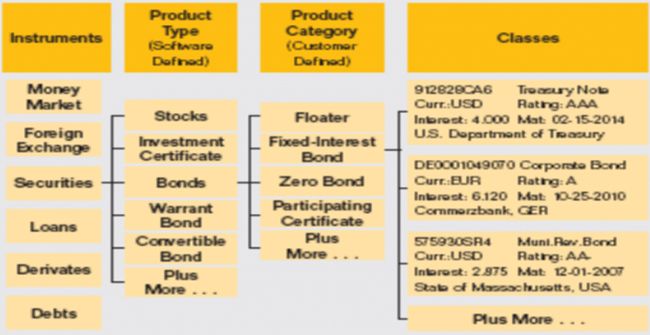
Money Market
- Money market transactions are used for short to medium-term investment and barrowing liquid funds.
- The money market area is a sub component of the Transaction manager and is closely integrated with other components.
- You can implement cash management decisions in the Money Market area based on the liquidity surplus or deficit determined in Cash Management.
- It is also closely linked to the Financial.
Features of Money Market
- Trading
- The trading area contains functions for entering money market transactions. It also enables you to also call up information on transactions or make changes at a later date. Collective processing functions are available to help you manage your transactions efficiently.
Types of products in the Money Market area are:
- Fixed Term Deposits
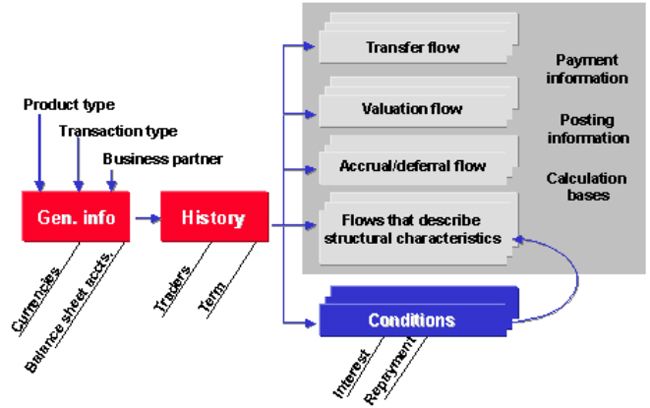
Master Data Management
Financial transaction processing in the transaction manager is based on master data.
Cash Management – Liquidity Forecast Process
Treasury consists of one module that could be potentiality used for the cash flow statement preparation-TR –CBM (Cash Budget Management). This module would allow to classify all the cash inflows and outflows using the “Commitment items" defined as SAP master data. Then the cash flow statement should be probably prepared in the report painter.
Cash Management
- Cash management is used monitor payment flows and safeguard liquidity, so that you can meet your payment commitments.
- Integration: cash management is a subcomponent of treasury.
- This means it is closely linked with treasury management (TR-TM) and market risk management (MRM).
- Cash management offers the functions described above for liquidity analysis purposes while MRM offers methods and process of assessing risks positions.
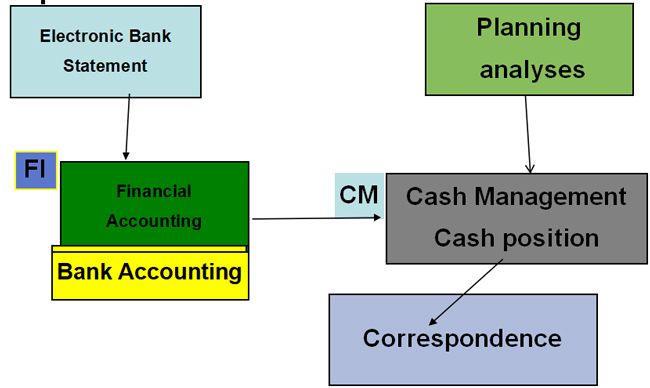
Cash Position
- Cash position supplies information on the current financial situation in your bank and bank clearing accounts. Integration with payment advices means that cash position can give you an Overview over Short-term liquidity movements.
- Integration:--The cash position reproduces the activity in your bank accounts. it is derived from the prompt entry (on their value date). of all payments made within a short period of time.
- Data is supplied from three sources.
The graphic below illustrate of the cash position in the Sap system
Cash Budget Management
- Is to identify control payment flows in light of liquidity considerations
- While cash management takes a short term view, Cash budget management deals with medium-term and long – term liquidity developments
- Before you can use cash budget management you must also having the financial accounting. The cash balances come from cash and bank accounts in financial accounting.Every posting made
CBM includes the following function
- Displaying business transactions having an affect on liquidity . By revenue and expenditure item
- Planning and displaying the payment flows and funds balances for any period you choose
- How to use cash budget management
- The SAP system distinguishes between different forms of organization, which have specific meanings within their respective applications. You can use them
Process flow
CBM and Funds Management
- Cash budget management covers the whole company. its main task is to identify impending shortages or surpluses of funds in your business.
- In funds management the business is divided into areas of responsibility, which are then monitored centrally. Budget funds are assigned to the individual areas of responsibility.
- The ultimate aim of funds management is to compare to actual data with the existing
Difference between CBM & CM
- Planning interval:-- Cash management deals only with the short-term liquidity of a business, while cash budget management is concerned with the medium term and long term.
- Division of revenue and expenditure:-- Cash management divides revenues and expenditures by customer and vendor group. While, cash budget management, the division is by revenue and expenditure item.
- Financial budget:--Planning is not possible in
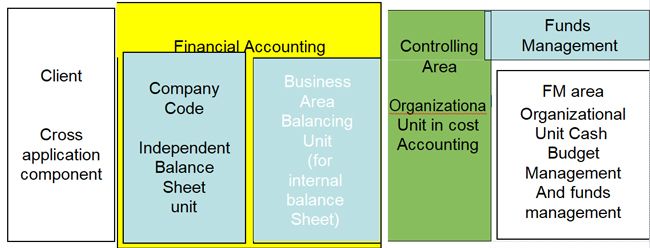
Financial Management Area
- The FM area is the commercial organizational unit, within which cash budget management and financial budgeting are conducted. It structures the business as a viewed from cash budget management.
- Financial accounting: The company code
- Cash budget management :The financial management area.
- Cash budget management you will be working with financial management areas
Commitment Item
- The basis data object in cash budget management is the commitment item.
- With commitment items, you can divided business transactions affecting liquidity in your business into revenue, expenditure, and balance items.
- Commitment Hierarchy:-- Commitment items are arranged in hierarchs. A distinction is drawn between
- Account assignment items:--Make up the lowest level in the commitment item hierarchy.
- Summarization items:--You define a hierarchy by
Commitment Item Master Record
You must define an item category and financial transaction in each commitment item master record. The item category controls whether the commitment is a revenue, expenditure, or balance item. The financial transaction is important When data is being recorded in cash budget management.
Authorization Check in Cash Budget Management
- By allocating authorizations, you determine which objects your personal may process and what processing functions they may use.
- Profiles consist of authorizations, for one work center.
- The authorizations in cash budget management are checked in the following order.
- Version authorization
Assigning Commitment Items to G/L Accounts
- For data to be recorded in cash budget management, you must always enter an account assignment when posting data in the feeder system.
- If do not define in the commitment item in the G/L account, you must specify one when entering a document, otherwise the system cannot post the document.
Business Transaction for CBM Feeder System
The following business transactions are supported in CBM
1.All financial accounting postings, in which “real” financial accounting documents are produced. For exaple
- Actual values in relation to payments in and out.
- Commitments values are bank clearing (Debit and credit side).
- Commitment arising invoice issued and received
- Commitments are down payments (debit and credit sides)
- Commitments are down payment requests (debit and credit sides)
- Recurring entry documents are not integrated.
2.From Materials Management.
- Commitments arising from purchase request ion.
- Commitments arising from purchase orders.
- Commitment arising from goods receipt.
Objectives
- To know our future cash inflows and outflows to assess Liquidity Forecast
- Process proposed should be automated fully
Process Requirements
- Reports for Daily, Weekly & monthly liquidity position at company Level
- Consolidation of these reports at Group level
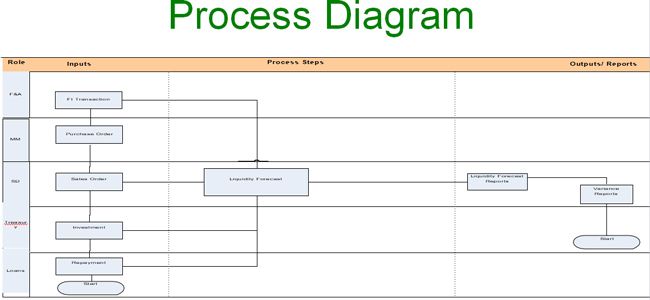
Process Diagram
Master Data in Cash Management
Structure for Liquidity Forecast
Planning Level
- To explain the beginning and ending account balances.
Source Symbols
- Divides the planning levels according to the sources
Planning Groups
- Customers and vendors are assigned to planning groups by means of master data entries
- The Items of the liquidity forecast report are picked up from the following components:
Financial Accounting – Open Items accounted & account balances Materials Management – Purchase Requisitions & Orders Sales and Distribution – Sales
Major Benefits
- Integration from all sources of Cash Flows
- Real time updated Data
- Actual Figures based on the updated data
- Automated Process
- Flexibility in Reports in term of Periodicity
- Flexibility in terms of Selection of Parameters