In SAP, User Type defines the categories of users like system administrators or operators. This classification system goes beyond just license types.
User types determine the permissions a user can be assigned through roles. These roles grant specific functionalities within the SAP system. With the help of various user types, the system administrator controls permission that can be assigned to each user to perform their task securely.
Different Types of Users in SAP
There are five types of users in SAP:
| User Types | Use |
|---|---|
| Dialog User | Single User logon, Interactive type of logon |
| System User | Multiple user logon, Used background processing and communication |
| Communication | Dialog-free communication between systems |
| Service User | Available for a larger, anonymous group of users. |
| Reference User | No logon is possible. |
1) Dialog user (A)
A regular dialogue user is used for all logon types by precisely one person. This is used to logon using the SAP GUI. During a dialog logon, the system checks for expired/initial passwords. The user can change his or her password. Multiple dialog logons are checked and, if appropriate, logged.
Characteristics of Dialog Users:
- These users are used for carrying out standard transactions.
- This is an interactive type of logon.
- The initial multiple logins are 6.
- They are set according to company policy.
2) System User (B)
These are non-interactive users. They are used for background processing and internal communication in the system (such as RFC users for ALE, Workflow, TMS, and CUA).
Characteristics of System Users
- The end users cannot change their passwords.
- Only the user administrator can change their passwords.
- Multiple logins are permitted in this type of user.
- Dialog logon is not possible for this type of user.
3) Communication User(C)
The communication user is used for dialog-free communication between systems. It is not possible to use this type of user for a dialog logon.
Characteristics of Communication User
- Their passwords are valid for a certain period, so they expire.
- The users have the option to change their passwords.
4) Service User (S)
The service user is available to a larger, anonymous group of users. The system does not check for expired/initial passwords during login. Only the user administrator can change the passwords.
Characteristics of Service User
- Generally, highly restricted authorizations are given to this type of user.
5) Reference User (L)
A reference user is, like the service user, a general non-person-related user. Dialog logon is not possible with this kind of user. A reference user is used only to assign additional authorizations. To attach a reference user to a dialog user, specify it when maintaining the dialog user on the Roles tab page.
Difference Between Various User Types
| Roles | Dialog User | System user | Communication User | Service User | Reference User |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logon with SAPGUI possible/ Interactive | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Multiple logins permitted | yes | NA | yes | yes | yes |
| Password | Expires or initialized | NA | NA | Expires or initialized | NA |
| Password can be changed by | End-user | User Administrator | End-User |
How to Create a User Type in SAP?
Please follow the steps below to create a user type in SAP:
- Execute t-code SU01 in the SAP command field.
- Next, enter the Username you want to create and then click on the Create icon.
- Now go to the Address menu and enter various user details first name, last name, email, etc.
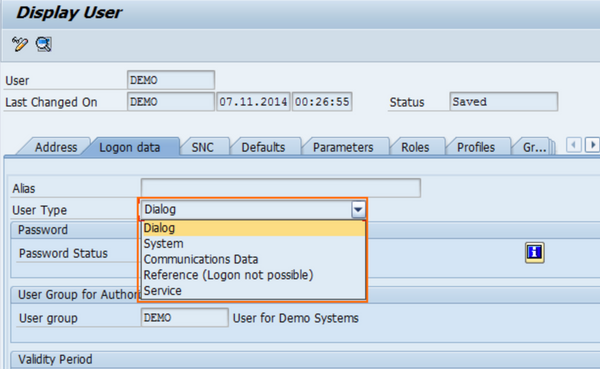
- Now you will be taken to the Logon Data window, here you will have to choose the SAP system user type from the drop-down list.
- Next, click New Password and create a new password.
- Once you have created a new password you will be directed to the Roles window, here the system administrators can assign specific roles to each user.
- Now navigate to the Profiles tab and then assign profiles to each user.
- At last, click on Save button to confirm the user type has been created.