In this article, we will learn about the TypeError: ‘float’ object can not be interpreted as an integer.
This error will occur in all the functions or methods. Where the function or method accepts only the integer value as a parameter. But instead, we have passed float values. The most common example is the range function. Since the range function only accepts an integer as a parameter.
For example, when we divide 16 by 8 using division operator ‘/’ in python, it’ll return a float value i.e. 2.0 and not an integer. This raises an error when we want an int as a parameter, but we have a float value.
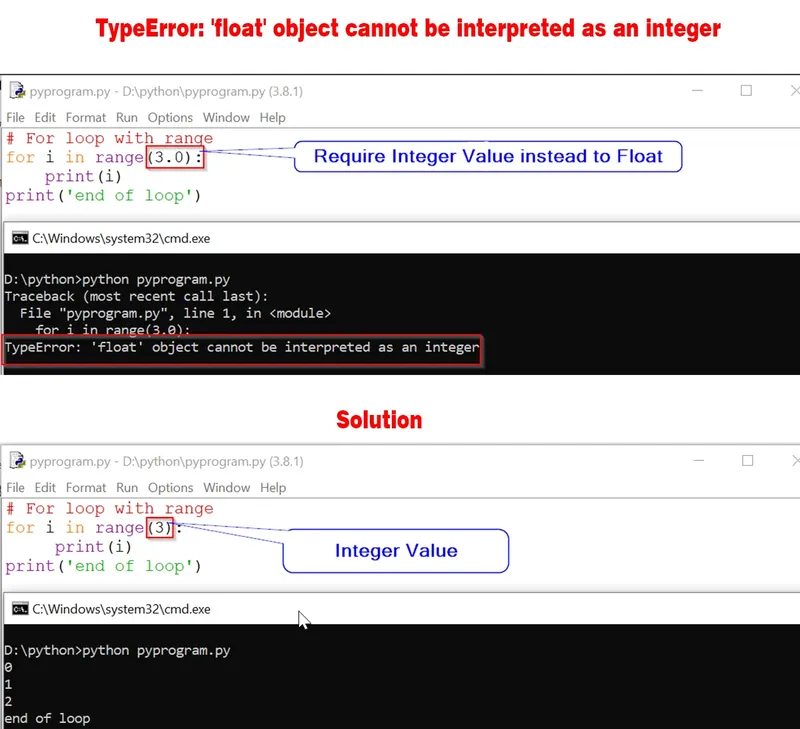
Let us understand it more with the help of an example.
Example 1:
for i in range(3.0):
print(i)
print('end of loop')
Output:
File "float.py", line 1, in <module>
for i in range(3.0):
TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
In the above example, we did not perform any arithmetic operations. Instead, we passed a float value as a range parameter. In this case, the cause for the TypeError is that the range function does not take float value as a parameter.
Solution:
for i in range(3):
print(i)
print('end of loop')
Output:
0
1
2
end of loop
Example 2:
for i in range(16/8):
print(i)
print('end of loop')
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "pyprogram.py", line 1, in <module>
for i in range(16/8):
TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
In the above example, when we performed division operation inside the range() function. We got a float value (2.0). But the range function takes only an integer value as a parameter.
Thus the error “TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer” is encountered.
Solution:
for i in range(5//8):
print(i)
print('end of loop')
Output:
0
1
end of loop
Unlike the division operator ‘/’ the floor division operator ‘//’ in python, returns an integer value. The floor division operator removes the digits after the decimal point. Thus we get an integer value.
So on dividing 16 by 8 using floor division operator ‘//’ we get ‘2’ as a parameter in range function. Thus no error is encountered, and we get the desired output.