MRP, or Material Requirements Planning, is a crucial function in the SAP MM (Materials Management) module that helps organizations plan and manage their inventory efficiently.
At its core, MRP is a software tool that uses production schedules, inventory data, and sales forecasts to determine the raw materials and components required to meet production goals.
By analyzing these inputs, MRP generates a list of materials to purchase and the timing of those purchases to ensure that production schedules can be met.
In SAP MM, MRP is integrated with other key functions like procurement, inventory management, and production planning, enabling organizations to optimize their supply chain processes and minimize costs.
Overall, MRP is an essential tool for any organization that wants to improve its inventory management processes and ensure that it can meet production goals on time and on budget.
MRP View
MRP View is a section in the SAP MM (Materials Management) module that provides an overview of the Material Requirements Planning (MRP) data for a specific material.
The MRP View allows users to see important information like the material's current stock level, its demand forecast, and the lead time required to procure it.
There is a three MRP view:
- MRP1: In this view,maintain the min. & Max stock of material that must be required for plant that is level of matarial that is required & before stock is less than the min. stock it is to be procured.
- MRP2: In this view, who is the requisioner plant/where it used that data will be maintain in this view so they can also make PR for that material.
- MRP3: The MRP3 view in provides additional planning data for a specific material. This view contains fields that help to fine-tune the MRP process for the material.
Advantages of SAP MRP:
The advantages of using SAP MRP are as follows:
-
Improved Inventory Management: SAP MRP provides real-time visibility into inventory levels and demand forecasts, enabling organizations to optimize their inventory levels and reduce excess inventory. This leads to significant cost savings and improved efficiency.
-
Better Production Planning: By using MRP, organizations can plan production more effectively, ensuring that they have the right amount of raw materials and components on hand to meet production goals. This reduces the risk of stock-outs and helps to improve customer satisfaction.
-
Streamlined Supply Chain Management: SAP MRP integrates with other key functions like procurement and inventory management, providing end-to-end visibility into the supply chain. This enables organizations to optimize their supply chain processes, reduce lead times, and improve overall efficiency.
-
Accurate Demand Forecasting: By analyzing historical data and current demand, SAP MRP helps organizations accurately forecast future demand. This allows them to plan production and procurement activities more effectively, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking.
-
Cost Savings: By optimizing inventory levels and improving production planning, SAP MRP helps organizations reduce costs associated with excess inventory, stock-outs, and expedited procurement.
MRP Process flow
The MRP process flow in SAP typically involves the following steps:
-
Demand Management: Sales and distribution provide customer requirements which are entered as Planned Independent Requirements (PIRs) in the Demand Management module.
-
Net Requirements Calculation: MRP calculates the net requirements for each material based on the PIRs, taking into account existing inventory levels and any open purchase orders or production orders.
-
Procurement Proposal: MRP generates a procurement proposal for each material, specifying the procurement quantity and date, based on the net requirements.
-
BOM Explosion: If a material is produced in-house, MRP explodes the Bill of Materials (BOM) and calculates the dependent requirements for each component required to produce the finished product.
-
Planned Orders: MRP creates planned orders for materials that need to be produced in-house and purchase requisitions for externally procured raw materials to fulfill the requirements.
-
Lead Time Scheduling: MRP calculates the planned order dates based on routing times and backward scheduling, starting from the requirement date minus the processing times and float time before production.
-
Conversion: Planned orders are converted into production orders or purchase orders, as applicable.
-
MRP Type: MRP type PD is essential to run MRP for the material, while MRP type ND can be maintained in the material master if MRP is not required for the material.
How to run MRP for all Products?
- Open transaction MD01 from the SAP Easy Access screen.
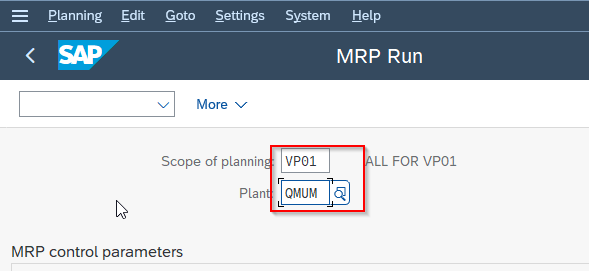
- Enter the Plant name for which you want to run MRP.
- Set the processing key as NETCH to run a net change in the total horizon.
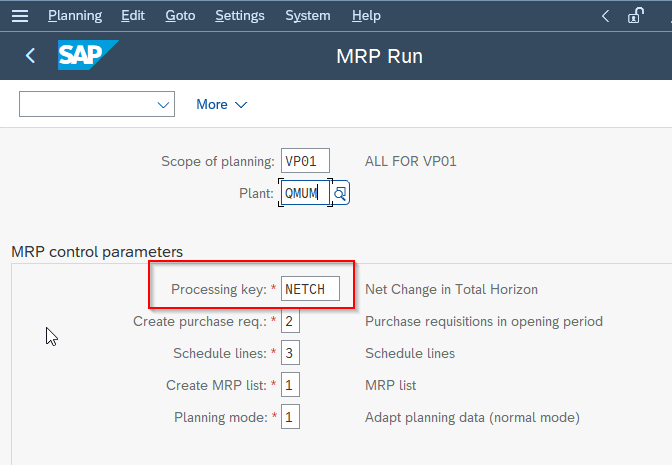
- Enter "1" in the Create Purchase req. field to generate purchase requisitions for externally procured materials instead of planned orders.
- Set the schedule lines field to "3" to generate schedule lines for raw materials with a scheduling agreement.
- Enter "1" in the MRP list field to create an MRP list for later analysis.
- Set the planning mode field to "3" to delete and recreate all planning data for all materials.
- Set the scheduling indicator to "2" to do lead time scheduling and consider routing times to calculate planned order dates.
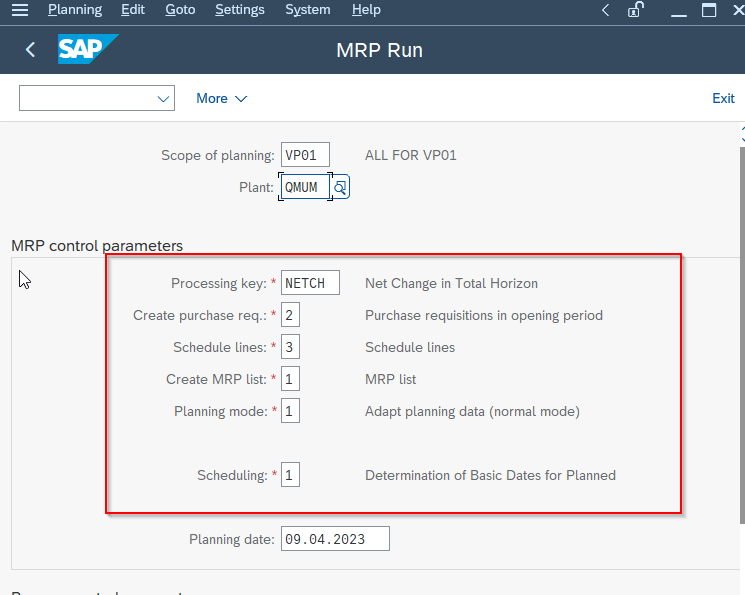
- Review your input parameters and press Execute button to confirm that you want to run MRP.
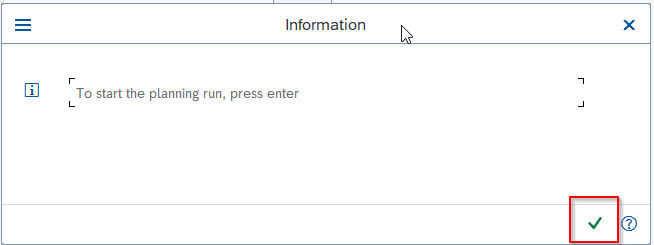
The system will ask user to re-check your input parameter because the MRP run is going to reschedule and overwrite all existing data.
Press Enter to proceed further
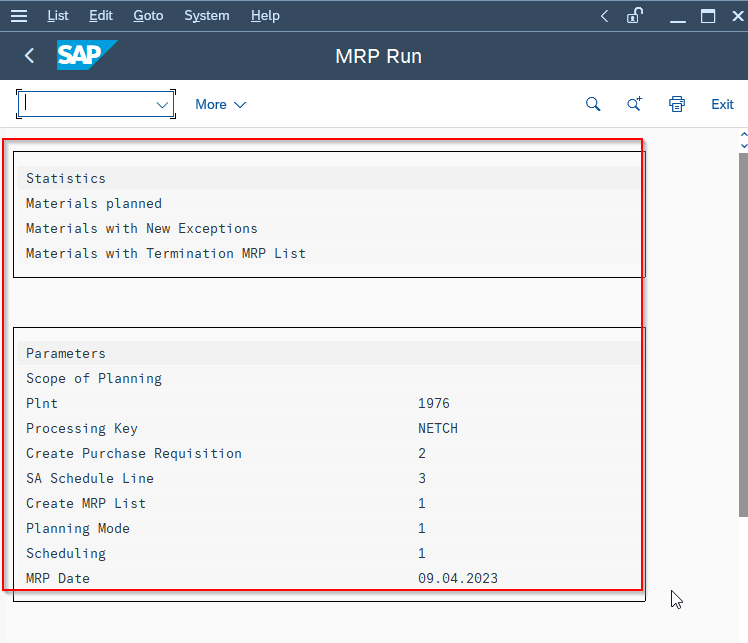
- Wait for the system to calculate the material requirements.
- Review the report that appears to see how many materials were planned and on what parameters were given during the MRP run.
If you want to get more simplicity and a more refined method of material requirements planning with in a plant you would have to MRP (Material Requirements Planning). By using this method the MRP area signifies a structural unit which will help you to bring all your Materials Requirements Planning independently. Infect you will be able to display is specifically for each MRP area.
By using MRP you will able to get one or more storage locations of a plant or a subcontractor for the materials planning of the parts to be offered, Although you can allocate a material to various MRP areas.
Each MRP area can, for example, parallel to a muster line, a provision storage setting or standard with a subcontractor. You can exactly plan self-governing supplies for extra parts or other superior supplies for distinct MRP areas.
At this time, you carry out Material Requirement’s Planning at plant level. The numerous supplies were merged in the planning run and procurement elements were generated for these attached supplies with unknown foundations. It will also permits you have to get exact control of the staging and procurement of important in –house production parts and purchased parts for every shop floor and assembly area. You can similarly plot the delivery of components for the separate subcontractors.
Hope this article might help you in understanding the MRP.