Variances in the Controlling Component (CO) refer to differences or discrepancies that occur in the financial performance or cost-related aspects within the CO module of an organization's enterprise resource planning (ERP) system.
These variances can arise due to several factors, including deviations from planned or targeted costs, overspending or underspending in specific cost centers or business processes, and the occurrence of over- or under-absorption of costs. Variance analysis is conducted to identify the causes of these discrepancies and assess their impact on the overall financial performance of the organization.
What is Variance Calculation?
Variance calculation is a method used to analyze and understand the reasons behind the observed variations or differences in the Controlling component (CO). This calculation is conducted based on the reconciled planning of internal activity, which involves the alignment and coordination of activities across different cost centers and business processes.
Variance Calculation help SAP users to identify the specific causes or factors contributing to the variances and allow for informed decision-making and corrective actions to improve future cost management and financial performance.
Types of Variance Calculation
In SAP, you can calculate several variances related to planning and production. Here are the four types of variances you mentioned:
- Planning Variances: These variances compare the planned quantities or costs with the actual quantities or costs. They help you evaluate the accuracy of your planning and identify any deviations from the planned values.
- Production Variances: These variances analyze the differences between the standard or target values and the actual values achieved during the production process. They provide insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the production operations.
- Production Variance of the Period: This variance focuses specifically on the production activities within a particular period, such as a day, week, or month. It compares the actual production costs or quantities incurred during that period with the standard or target values set for that same period.
- Total Variance: The total variance combines all the individual variances mentioned above to provide an overall assessment of the variations between planned and actual quantities or costs. It represents the cumulative effect of planning and production discrepancies and can help you understand the overall performance of your operations.
How to Perform Variance Calculation?
Please follow the steps below to perform variance calculation:
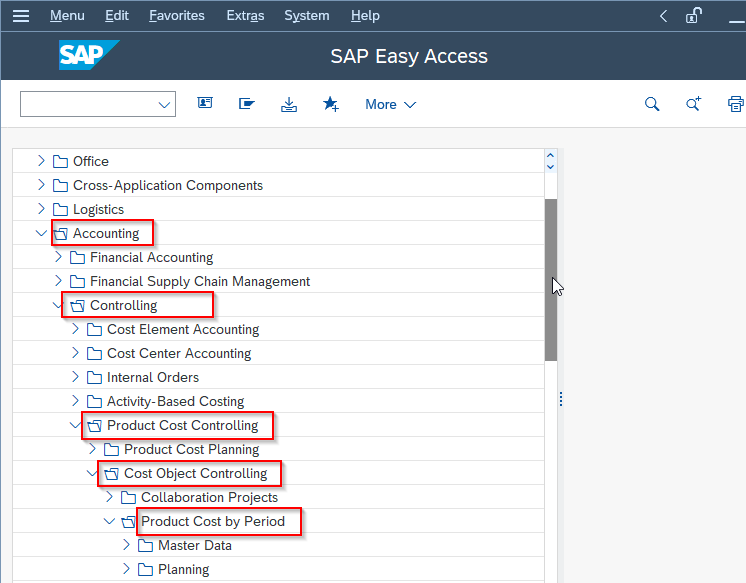
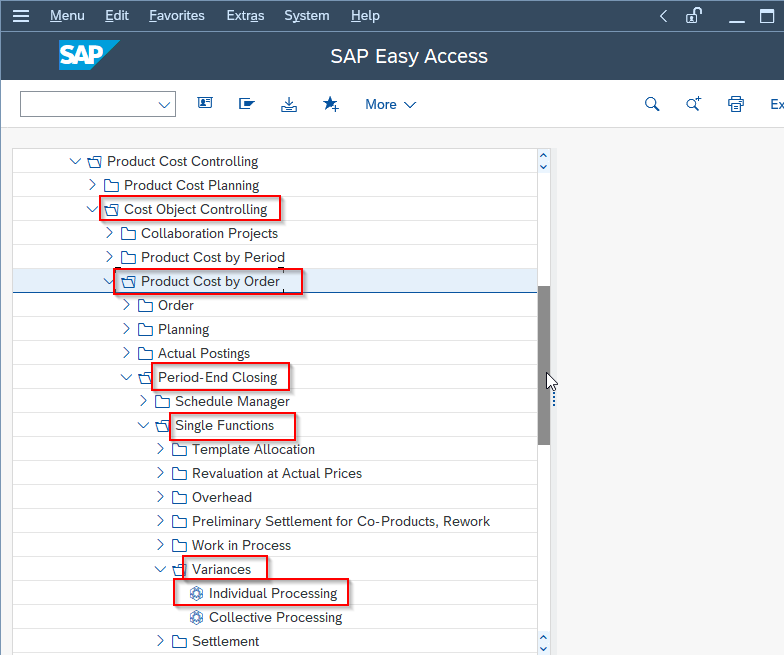
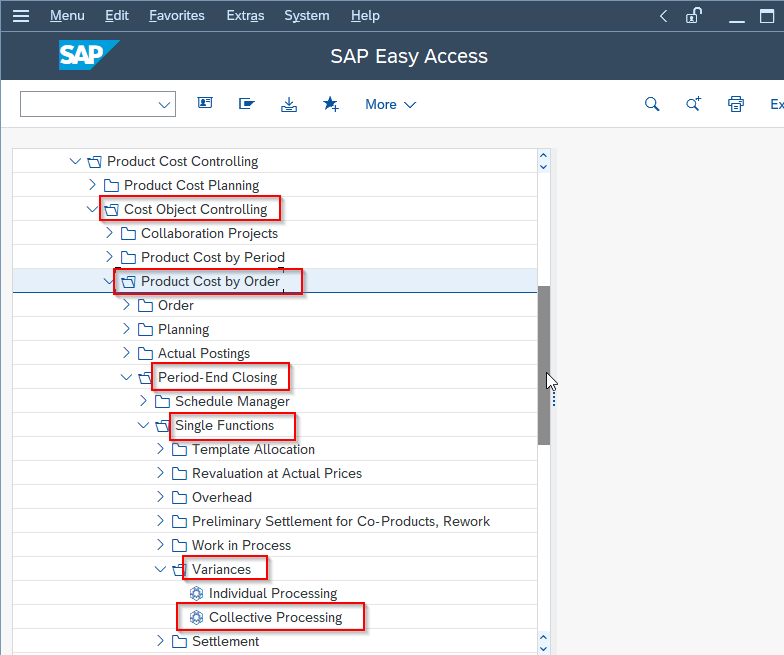
Navigate to the following IMG path:
Accounting > Controlling > Product Cost Controlling > Cost Object Controlling > Product Cost by Period > Period-end closing > Single Functions: Product Cost Collector > Variances > Individual Processing or Collective Processing.
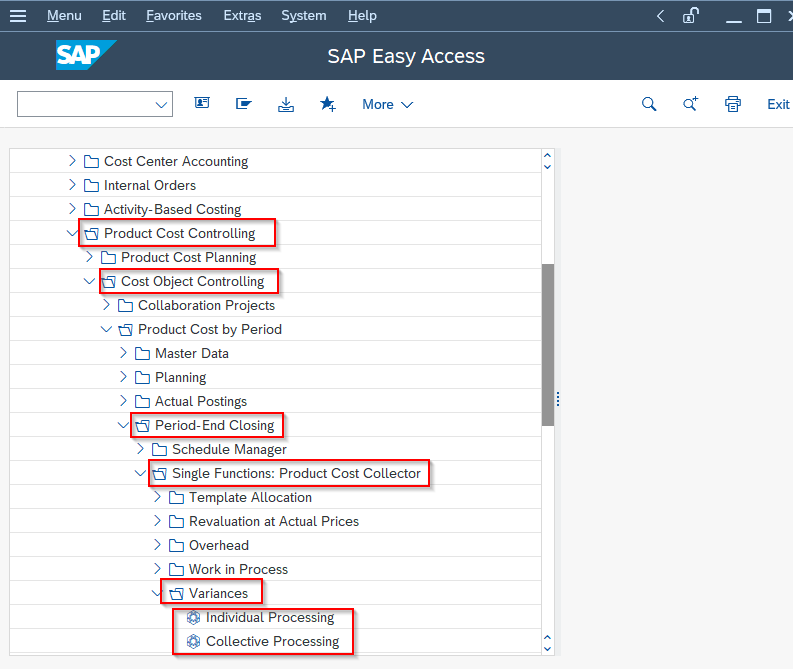
Or navigate to the following IMG path:
Accounting > Controlling > Product Cost Controlling > Cost Object Controlling > Product Cost by Period > Period-end closing > Single Functions: Product Cost Collector > Variances > Individual Processing or Collective Processing.
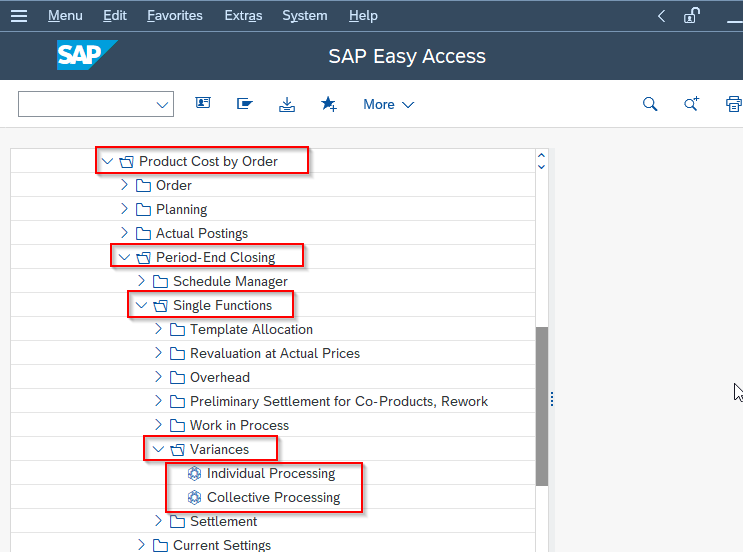
If the user is required to calculate the variances for a single cost object, click on the Individual Processing option.
If the user is required to calculate the variances for all cost object in a controlling area, click on the Collective Processing option.
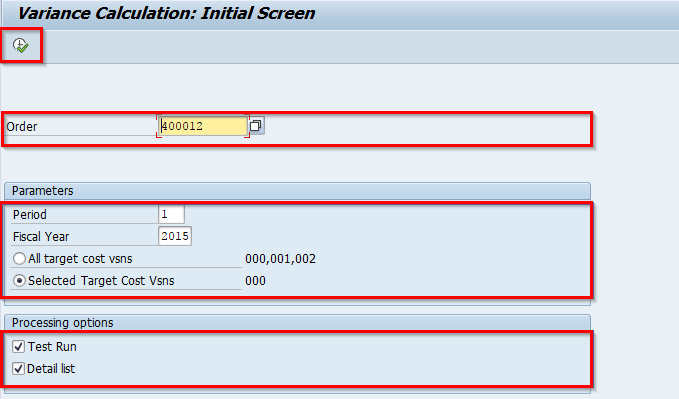
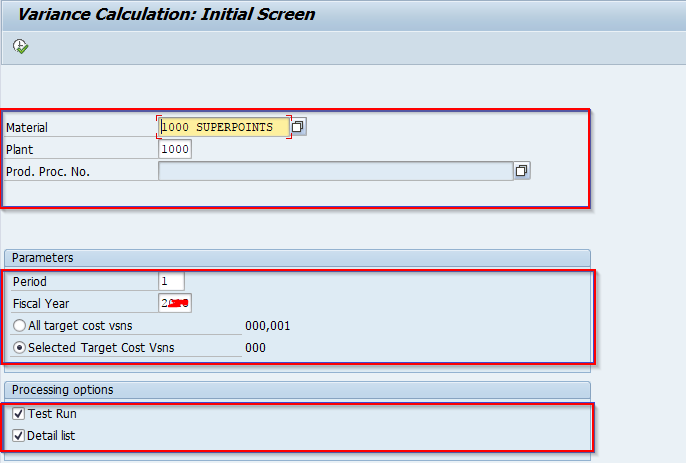
Now if Product Cost by Period, enter the following details
- Material
- Plant
- Parameters
- Processing options
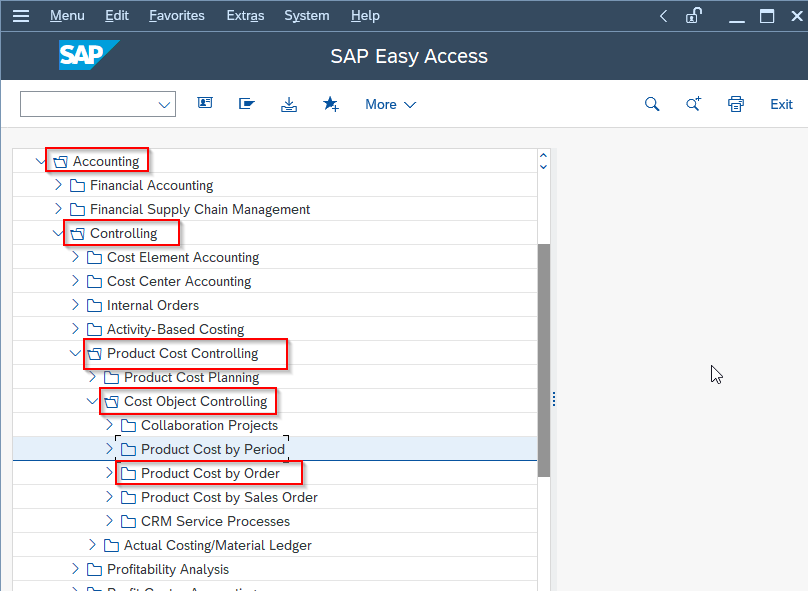
Or if Product Cost by Order, Enter the following details
- Order
- Parameters
- Processing
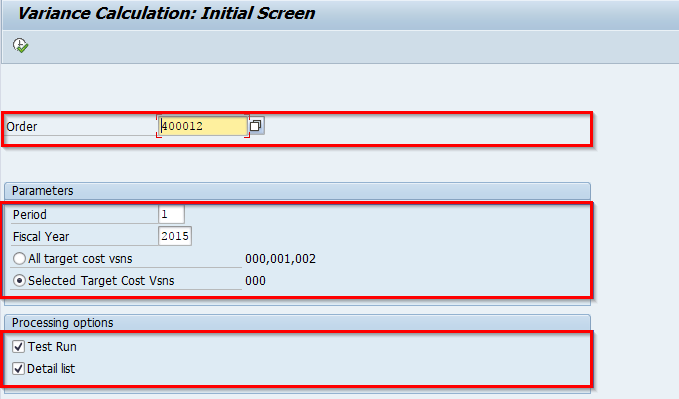
Once the information is entered, click on the Execute button to calculate the variances.